Observability
Introduction
Note
You will not install a full blown monitoring and logging solution on the development cluster such as Prometheus and Loki, but will do so for the staging and production clusters.
On the development environment you will be configuring the Kubernetes Metrics Server and Kubernetes Dashboard tools. This way your cluster size can be small but sufficient that you can do your local development and deploy that to a Kubernetes cluster and test it. At the most basic level you will need to be able to troubleshoot your aplication if things go wrong. In this section, you will learn about the Kubernetes Metrics Server and the Kubernetes Dashboard. Metrics Server is a scalable, efficient source of container resource metrics for Kubernetes built-in autoscaling pipelines. It collects resource metrics from Kubelets and exposes them in Kubernetes apiserver through Metrics API. Kubernetes Dashboard is a general purpose, web-based UI for Kubernetes clusters. It allows users to manage applications running in the cluster and troubleshoot them, as well as manage the cluster itself.
Prerequisites
To complete this section you will need:
- Helm installed as explained in the Installing required tools section.
- A Kubernetes cluster (DOKS) up and running as explained in the Set up DOKS section.
- JQ command-line JSON processor installed on your machine.
- The online boutique sample application deployed to your cluster as explained in the Tilt remote development section.
Installing the Kubernetes Metrics Server
In this section you will install the community maintained Kubernetes Metrics Server. Please follow below steps to install it using Helm:
-
Add the Metrics Server
Helmrepository: -
Install the
Kubernetes Metrics ServerusingHelm:helm upgrade --install metrics-server metrics-server/metrics-server \ --namespace metrics-server \ --create-namespaceNote
To check if the installation was successful, run the
helm ls -n metrics-servercommand, and confirm the deployment status.
Collect resource metrics from Kubernetes objects
Resource metrics track the utilization and availability of critical resources such as CPU, memory, and storage. Kubernetes provides a Metrics API and a number of command line queries that allow you to retrieve snapshots of resource utilization.
Query the Metrics API to retrieve current metrics from any node or pod (you can find your desired node or pod by running kubectl get nodes or kubectl get pods):
kubectl get --raw /apis/metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/nodes/<NODE_NAME> | jq
kubectl get --raw /apis/metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/namespaces/<NAMESPACE>/pods/<POD_NAME> | jq
Info
The Metrics API returns a JSON object, so (optionally) piping the response through jq displays the JSON in a more human-readable format.
Retrieve compact metric snapshots from the Metrics API using kubectl top. The kubectl top command returns current CPU and memory usage for a cluster’s pods or nodes, or for a particular pod or node if specified.
The output should look like the following:
NAME CPU(cores) CPU% MEMORY(bytes) MEMORY%
basicnp-766qo 280m 7% 1662Mi 24%
basicnp-766qr 252m 6% 1561Mi 23%
Or you can query resource utilization by pod in a particular namespace (you can use the microservices-demo-dev namespace you deployed in the Tilt Remote section):
The output should look like the following:
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
cartservice-84758f76f-cl9vm 8m 29Mi
checkoutservice-5d8d8cfd5f-8hbjn 3m 16Mi
currencyservice-5d5f698f87-kh4z8 4m 30Mi
emailservice-f8795cc94-r7hwp 30m 40Mi
frontend-6d45d8cc5d-59fmw 1m 20Mi
paymentservice-995d69494-kcqn2 5m 30Mi
productcatalogservice-556d4f9446-7sqp9 7m 16Mi
recommendationservice-59f78c445b-5487v 40m 40Mi
redis-cart-596c7658c4-lwf8g 3m 7Mi
shippingservice-bfc488696-dkcpz 3m 15Mi
See details about the resources that have been allocated to your nodes, rather than the current resource usage. The kubectl describe command provides a detailed breakdown of a specified pod or node.
The output is quite verbose containing a full breakdown of the node’s workloads, system info, and metadata such as labels and annotations.
Click to expand node describe command output
Name: basicnp-766qo
Roles: <none>
Labels: beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64
beta.kubernetes.io/instance-type=s-4vcpu-8gb-amd
beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux
doks.digitalocean.com/node-id=018db650-0dd3-4e23-a387-d386a193456e
doks.digitalocean.com/node-pool=basicnp
doks.digitalocean.com/node-pool-id=45a15812-c08d-48f0-ae7d-61eb0ddc3e7c
doks.digitalocean.com/version=1.24.4-do.0
failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/region=nyc1
kubernetes.io/arch=amd64
kubernetes.io/hostname=basicnp-766qo
kubernetes.io/os=linux
node.kubernetes.io/instance-type=s-4vcpu-8gb-amd
region=nyc1
topology.kubernetes.io/region=nyc1
type=basic
Annotations: alpha.kubernetes.io/provided-node-ip: 10.116.0.4
csi.volume.kubernetes.io/nodeid: {"dobs.csi.digitalocean.com":"318312990"}
io.cilium.network.ipv4-cilium-host: 10.244.1.102
io.cilium.network.ipv4-health-ip: 10.244.1.76
io.cilium.network.ipv4-pod-cidr: 10.244.1.0/25
node.alpha.kubernetes.io/ttl: 0
volumes.kubernetes.io/controller-managed-attach-detach: true
CreationTimestamp: Mon, 26 Sep 2022 11:48:39 +0300
Taints: <none>
Unschedulable: false
Lease:
HolderIdentity: basicnp-766qo
AcquireTime: <unset>
RenewTime: Wed, 28 Sep 2022 11:31:13 +0300
Conditions:
Type Status LastHeartbeatTime LastTransitionTime Reason Message
---- ------ ----------------- ------------------ ------ -------
NetworkUnavailable False Mon, 26 Sep 2022 11:50:10 +0300 Mon, 26 Sep 2022 11:50:10 +0300 CiliumIsUp Cilium is running on this node
MemoryPressure False Wed, 28 Sep 2022 11:26:35 +0300 Mon, 26 Sep 2022 11:48:39 +0300 KubeletHasSufficientMemory kubelet has sufficient memory available
DiskPressure False Wed, 28 Sep 2022 11:26:35 +0300 Mon, 26 Sep 2022 11:48:39 +0300 KubeletHasNoDiskPressure kubelet has no disk pressure
PIDPressure False Wed, 28 Sep 2022 11:26:35 +0300 Mon, 26 Sep 2022 11:48:39 +0300 KubeletHasSufficientPID kubelet has sufficient PID available
Ready True Wed, 28 Sep 2022 11:26:35 +0300 Mon, 26 Sep 2022 11:49:10 +0300 KubeletReady kubelet is posting ready status. AppArmor enabled
Addresses:
InternalIP: 10.116.0.4
Hostname: basicnp-766qo
ExternalIP: 159.223.163.15
Capacity:
cpu: 4
ephemeral-storage: 165089200Ki
hugepages-1Gi: 0
hugepages-2Mi: 0
memory: 8149728Ki
pods: 110
Allocatable:
cpu: 3900m
ephemeral-storage: 152146206469
hugepages-1Gi: 0
hugepages-2Mi: 0
memory: 6694Mi
pods: 110
System Info:
Machine ID: a6b0d5360452428382d5b0c516caa546
System UUID: a6b0d536-0452-4283-82d5-b0c516caa546
Boot ID: 3345884c-f9af-4716-af86-17814d28ef96
Kernel Version: 5.10.0-0.bpo.15-amd64
OS Image: Debian GNU/Linux 10 (buster)
Operating System: linux
Architecture: amd64
Container Runtime Version: containerd://1.4.13
Kubelet Version: v1.24.4
Kube-Proxy Version: v1.24.4
ProviderID: digitalocean://318312990
Non-terminated Pods: (15 in total)
Namespace Name CPU Requests CPU Limits Memory Requests Memory Limits Age
--------- ---- ------------ ---------- --------------- ------------- ---
cert-manager cert-manager-ddd4d6ddf-zmpk4 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 47h
ingress-nginx ingress-nginx-controller-778667bc4b-7lj4c 100m (2%) 0 (0%) 90Mi (1%) 0 (0%) 47h
kube-system cilium-bv8x9 310m (7%) 100m (2%) 310Mi (4%) 75Mi (1%) 47h
kube-system cilium-operator-6d485f4f69-fsv7x 100m (2%) 0 (0%) 150M (2%) 150M (2%) 47h
kube-system coredns-9c8d9dc8c-9mzcd 100m (2%) 0 (0%) 150M (2%) 150M (2%) 47h
kube-system cpc-bridge-proxy-dktvq 100m (2%) 0 (0%) 75Mi (1%) 0 (0%) 47h
kube-system csi-do-node-trfdm 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 47h
kube-system do-node-agent-vt9kn 102m (2%) 102m (2%) 80Mi (1%) 300Mi (4%) 47h
kube-system konnectivity-agent-fnvp9 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 47h
kube-system kube-proxy-9ff7c 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 125Mi (1%) 0 (0%) 47h
microservices-demo-dev cartservice-84758f76f-cl9vm 200m (5%) 300m (7%) 128Mi (1%) 256Mi (3%) 45h
microservices-demo-dev frontend-6d45d8cc5d-59fmw 100m (2%) 200m (5%) 64Mi (0%) 128Mi (1%) 45h
microservices-demo-dev productcatalogservice-556d4f9446-7sqp9 100m (2%) 200m (5%) 64Mi (0%) 128Mi (1%) 45h
microservices-demo-dev recommendationservice-59f78c445b-5487v 100m (2%) 200m (5%) 220Mi (3%) 450Mi (6%) 45h
microservices-demo-dev redis-cart-596c7658c4-lwf8g 70m (1%) 125m (3%) 200Mi (2%) 256Mi (3%) 45h
Allocated resources:
(Total limits may be over 100 percent, i.e., overcommitted.)
Resource Requests Limits
-------- -------- ------
cpu 1382m (35%) 1227m (31%)
memory 1721869056 (24%) 1970381568 (28%)
ephemeral-storage 0 (0%) 0 (0%)
hugepages-1Gi 0 (0%) 0 (0%)
hugepages-2Mi 0 (0%) 0 (0%)
Installing the Kubernetes Dashboard
Note
The Kubernetes Dashboard is already available as a managed solution for DigitalOcean customers after creating a Kubernetes Cluster. You are installing it separately due to the lack of CPU and memory usage metrics not displayed in the managed solution and those metrics are very important to monitor. Please see this support case for more details.
In this section you will install the community maintained Kubernetes Dashboard. Please follow below steps to install it using kubectl:
-
Install the
Kubernetes Dashboardusingkubectl:kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.6.1/aio/deploy/recommended.yamlNote
To check if the installation was successful, run the
kubectl get pods -n kubernetes-dashboardcommand, and confirm that the pods are running. -
In a new terminal window start the
kubectl proxy: -
Launch a web browser and open the Kubernetes Dashboard Login page. Then, choose the
Kubeconfigoption, and provide your cluster's config file to log in.Note
To get the config file navigate to your DigitalOcean cloud console, go to
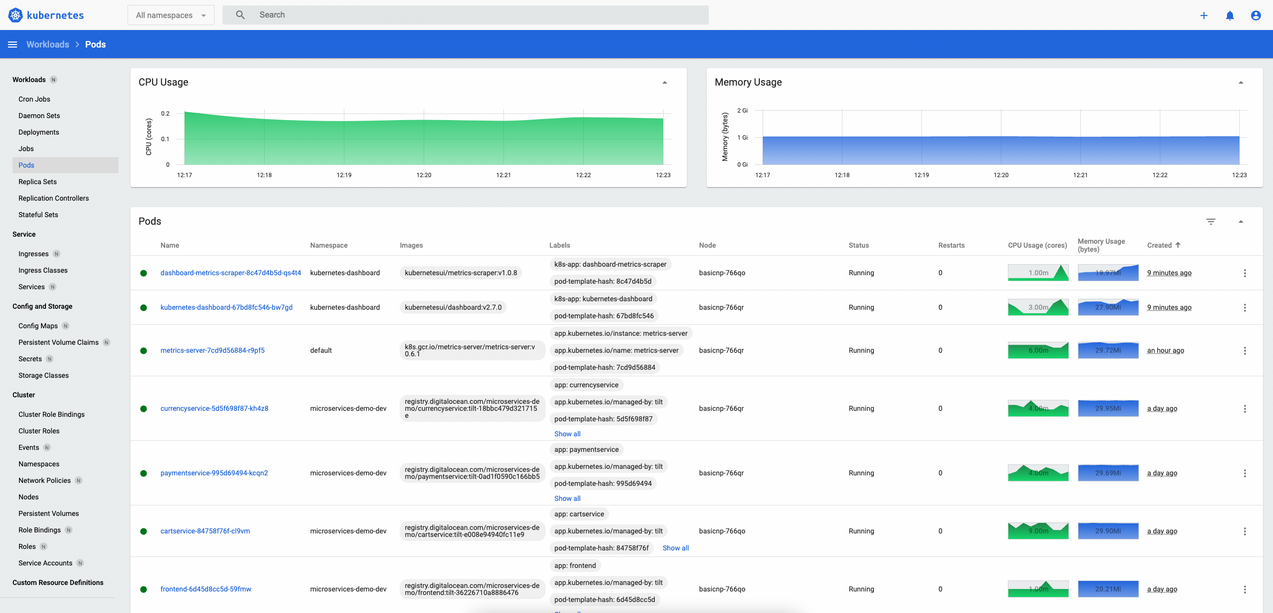
Kubernetes, select your cluster and from theConfigurationsection, click onDownload Config File.After successfully logging in, you should be presented with the main dashboard landing page:
Next, you can check metric summaries for each pod, node, and namespace in your cluster. Editing Kubernetes objects is also possible, such as scaling up/down deployments, change image version for pods, etc.
Going further it is also possible to inspect log streams for pods. From the navigation bar at the top of the Pods view, click on the Logs tab to access a pod log stream directly in your web browser. In case of pods comprised of multiple containers, you have the option to inspect each container logs. Finally, you can Exec into a pod container from the same page.
Kuberentes events are also viewable from the Kubernetes Dashboard. From the left menu click on the Events view. Events will be displayed and stored for 1 hour.
Next, you will learn how to provision and configure the staging environment for the online boutique sample application. Besides DOKS setup and the sample app deployment, you will also configure a full observability stack comprised of logging, monitoring and alerting via Slack. Usually, a staging environment should be pretty close (if not similar) to a production environment.